
CME 27/11/14 Paediatric Fractures Charlie's ED
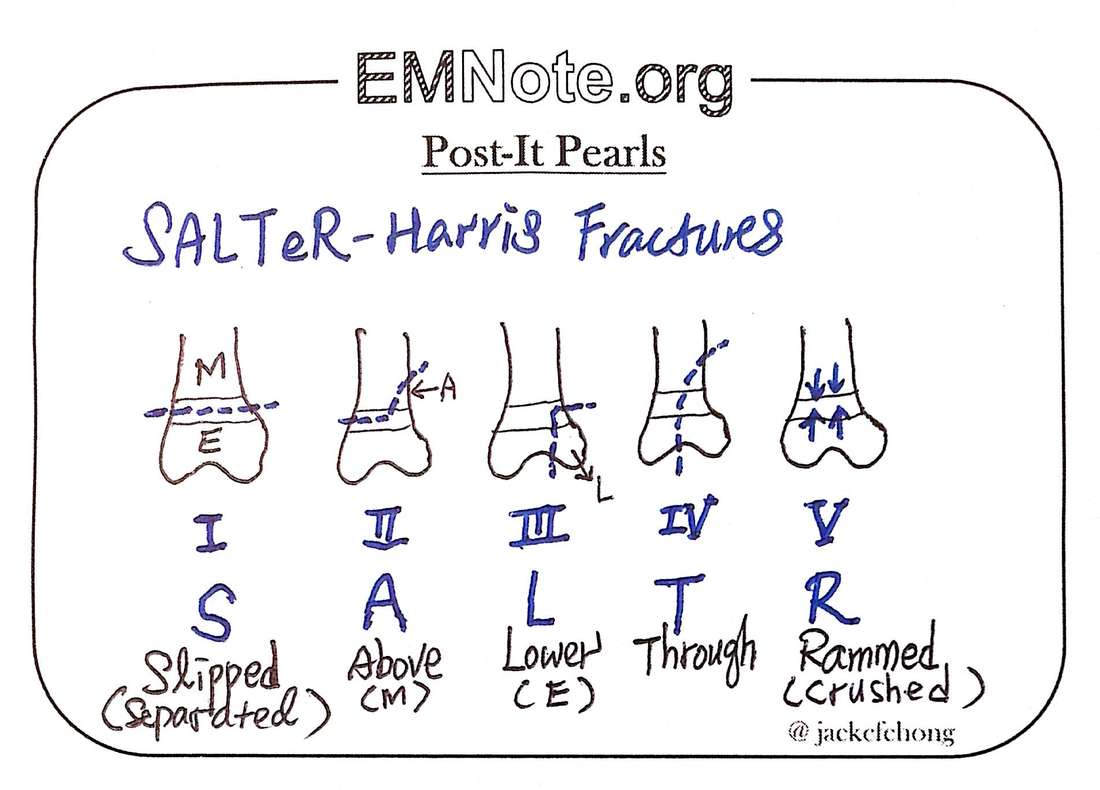
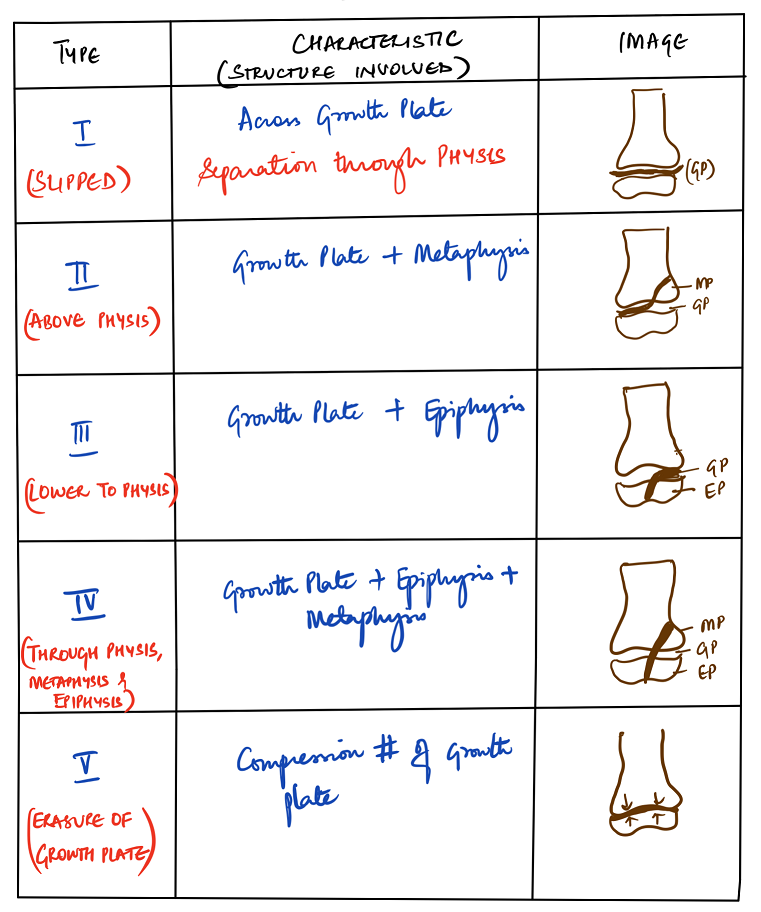
Salter-Harris classification. The most frequently used classification of physeal injuries is that of Salter and Harris [14], which describes five different types. It fails, however, to differentiate injuries to the zone of Ranvier at the periphery of the physis. These may be due to ligamentous avulsion or open abrasive trauma.
EMNote
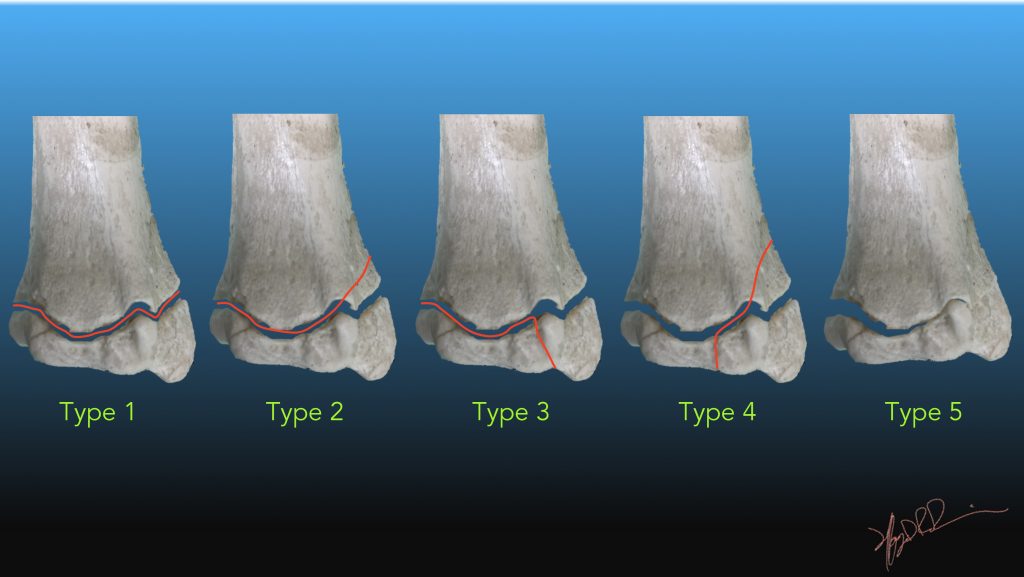
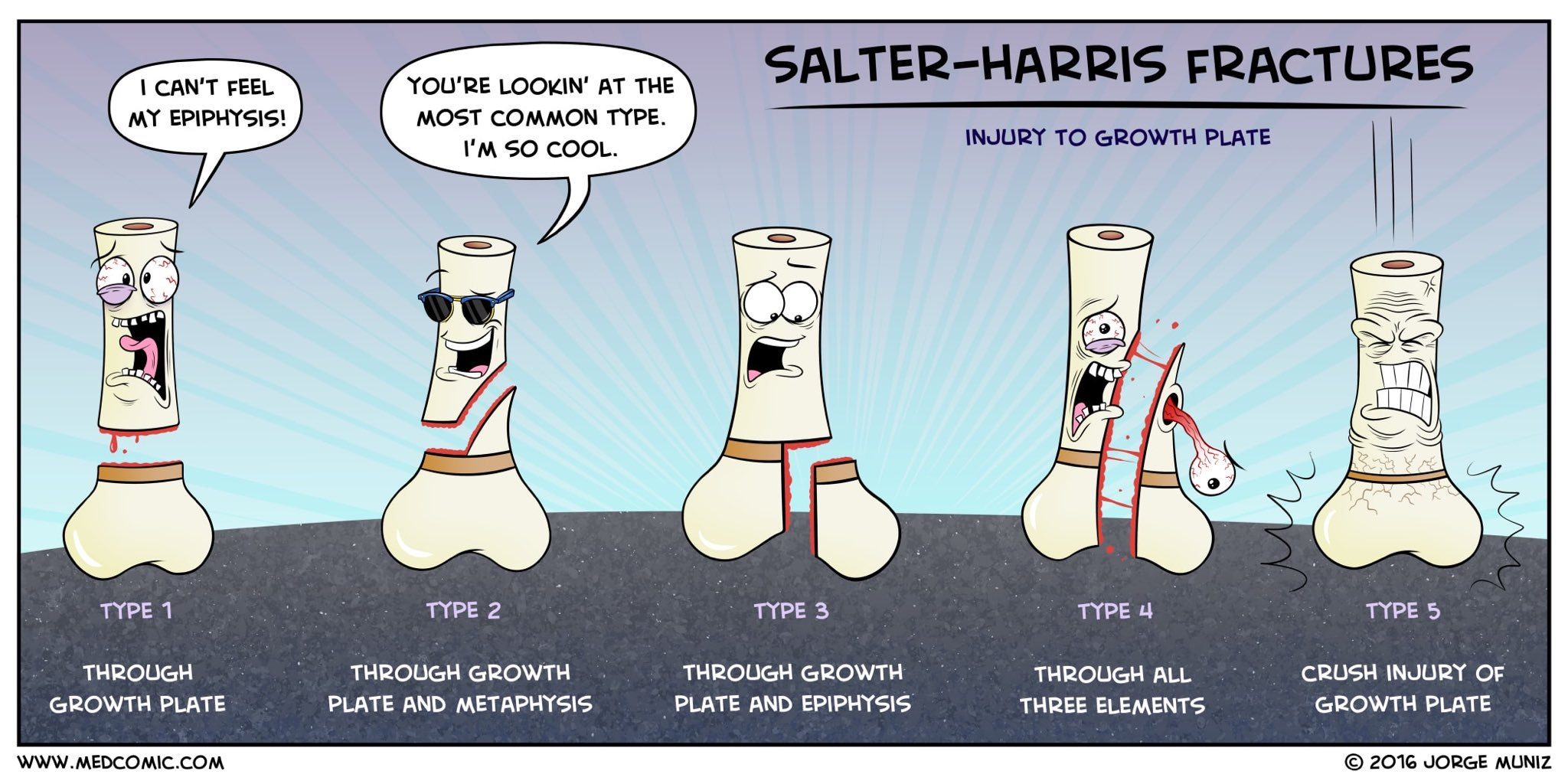
The five basic fracture types of the Salter-Harris classification are shown. A Type I fracture is a separation through the physis. A Type II fracture enters in the plane of the physis and exits through the metaphysis. The resulting metaphyseal fragment is called the Thurston-Holland fragment (*).
SalterHarris Classification of Growth Plate Fractures UW Emergency Radiology
A Salter-Harris fracture is a fracture that involves the epiphyseal plate (growth plate) of a bone, specifically the zone of provisional calcification. [2] It is thus a form of child bone fracture. It is a common injury found in children, occurring in 15% of childhood long bone fractures. [3]
SalterHarris Fracture Classification REBEL EM Emergency Medicine Blog
Growth plate injuries: Salter-Harris classification. Physeal fractures of the distal radius and ulna: long-term prognosis. Salter-Harris fractures (physeal fractures) refer to fractures through a growth plate (physis) and are, therefore, specifically applied to bone fractures in children.

OurMedicalNotes SalterHarris Classification
Classification de Salter-Harris pour les fractures-décollement des disques ou plaques épiphysaires (cartilages de conjugaison) Les types I à IV sont des fractures épiphysaires; la plaque de croissance est séparée de la métaphyse. Le type II est le plus fréquent et le type V le moins fréquent.
Salter Harris Classification Antrim ED Meducation
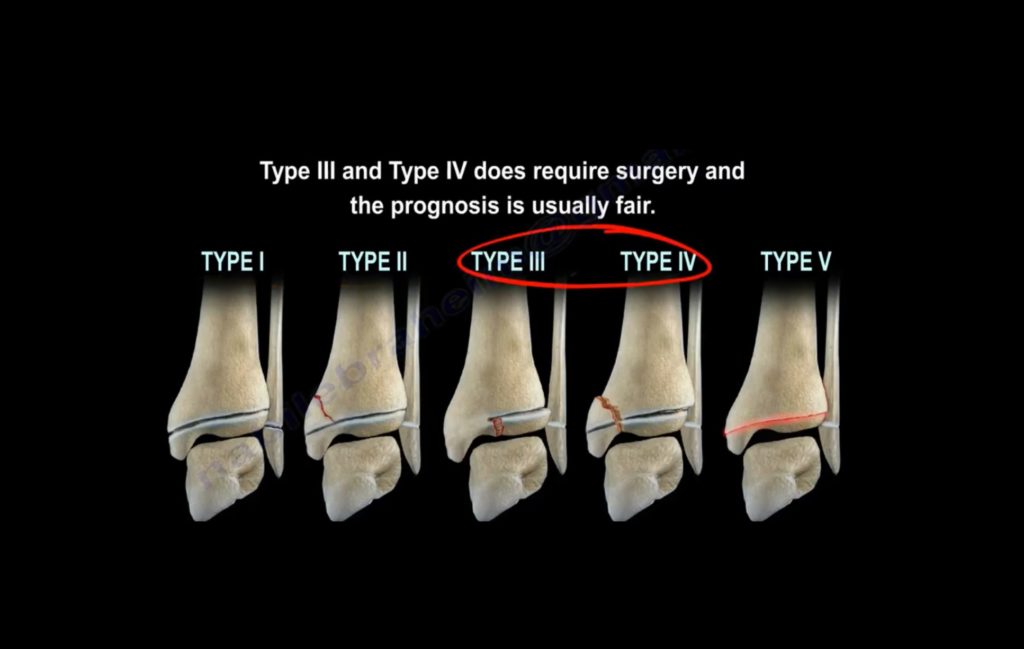
Salter-Harris Classification. The most common physeal ankle fracture is the Salter-Harris Type II (SH-II), which account for 32-40% of pediatric distal tibial fractures, then followed by SH-III (25%), SH-IV (up to 25%), SH-I (3-15%) and SH-V (less than 1%). 8, 38 The prognosis of SH-I and SH-II is the best, followed by SH-III then SH-IV.

SalterHarris Classification SalterHarris Fractures GrepMed
Salter-Harris fractures are injuries where a fracture of the metaphysis or epiphysis extends through the physis. Not all fractures that extend to the growth plate are Salter-Harris fractures. Radiographic features. Salter-Harris type I fractures describe a fracture that is completely contained within the physis. There is no associated bone.

Salter Harris Physeal Injury Classification S GrepMed
In a study of distal radius fractures, Cannata et al. found that the rate of physeal arrest at the distal radius was less than 30% while the rate of physeal arrest at the distal ulna approached 80%, however, neither was significantly correlated to Salter-Harris classification and fewer than 5% of patients had residual symptoms or functional.
Medicowesome SalterHarris classification of fractures
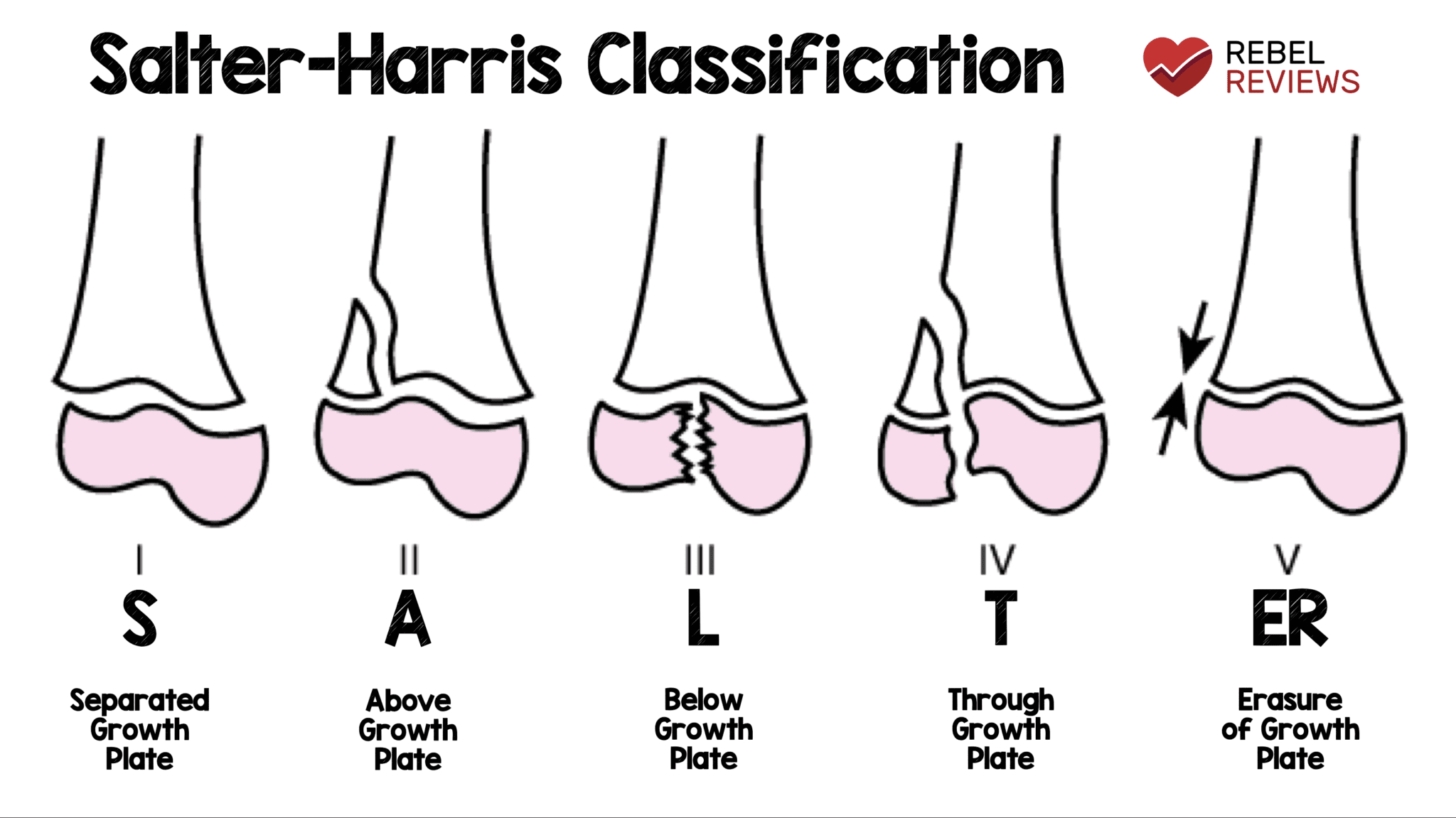
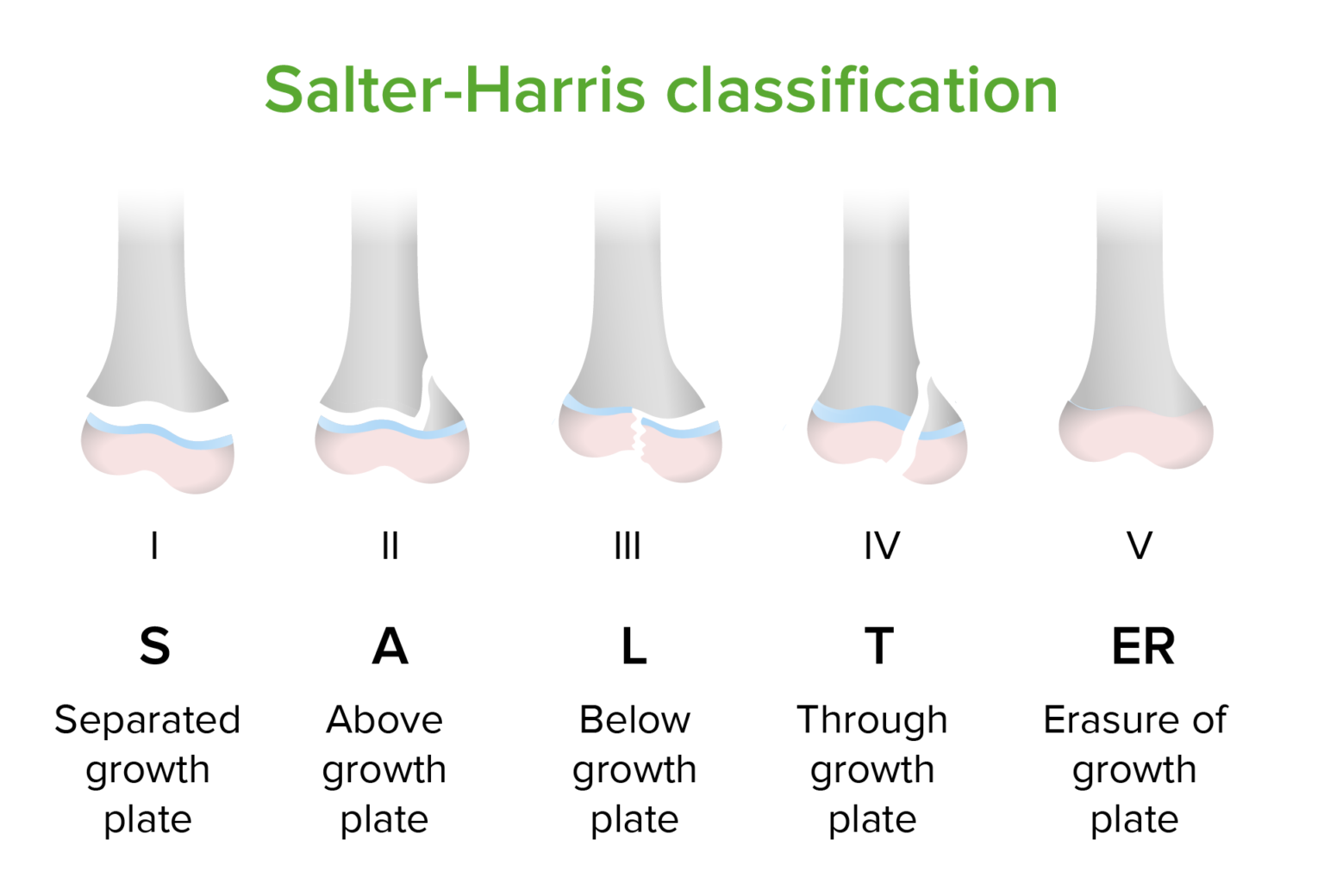
SMACK S: slipped (type I) M: metaphyseal (type II) A: articular-epiphyseal (type III) C: complete-metaphysis and epiphysis (type IV) K: krushed! (type V) SMETI S: slipped (type I) M: metaphyseal (type II) E: epiphyseal (type III) T: through or transverse or together (type IV) I: impacted (type V) Quiz questions References Incoming Links

Pin on Rad
The Salter-Harris classification system is used to grade fractures that occur in children which involve the growth plate ('physis') of a long bone (e.g. tibia or humerus). The classification is based on the involvement of the metaphysis, physis or epiphysis. Salter-Harris fractures are usually the result of a traumatic incident, like a fall.

Pin en Medicine
The Salter-Harris classification was proposed by Salter and Harris in 1963 1 and, at the time of writing (January 2023) remains the most widely used system for describing physeal fractures . Classification Conveniently the Salter-Harris types can be remembered by the mnemonic SALTR. type I s lipped 5-7%
Salter Harris Fracture Classification Rebel Em Emergency Medicine Blog kulturaupice
The epiphyseal plate (physis or growth plate) is the weakest part of. the bone to shearing injuries. The Salter-Harris classification is a means of categorizing. epiphyseal plate fractures and provides clues to their prognosis. All such these fractures, by definition, involve or extend through the epiphyseal plate so that all such fractures.

PEDIATRIC EPIPHISIAL FRACTURE (SALTERHARRIS) CLASSIFICATION Imagenes de medicos, Radiología
The Salter-Harris classification describes fractures in children around a growth plate, or physis. This descriptive classification system often has treatment implications as well" Overview Physis, or "growth plate," is area of growing cartilage in children's bones responsible for growth throughout childhood until reaching skeletal maturity
salter harris types ALiEM
A Salter-Harris type I fracture refers to a fracture line that runs straight across the growth plate, involving the cartilage without affecting the bone. Type I may cause the epiphysis, or the rounded end of the bone, to separate from the rest of the bone.

SalterHarris Classification PT Master Guide
Injury Classification. Salter-Harris classification . Type 1: physeal separation. Type 2: fracture traverses physis and exits metaphysis. most common type. Thurston Holland fragment. Type 3: fracture traverses physis and exits epiphysis. Type 4: fracture passes through epiphysis, physis, metaphysis.
Salter Harris Classification of Epiphyseal Injuries —
Description Salter-Harris classification of fractures describes injuries involving the epiphyseal plate of any bone. Epiphyseal injuries are significant in patients who are still 'growing' and significant complications, such as disturbance of growth, are avoided by recognition of such an injury to the epiphyseal plate